Blog
Ancient Artz | Timeless Creativity & Cultural Heritage

Art has always been more than an aesthetic endeavor—it is a lens through which we understand our predecessors, their beliefs, and the world they lived in. Ancient art, in particular, holds a timeless allure, bridging the past to the present with creativity and cultural heritage that never ceases to inspire. From the intricate pottery of the ancient Egyptians to the grand temples of the Greeks and the enduring tales etched into cave walls, ancient art is a testament to the human spirit and ingenuity.
This blog explores the world of ancient art, highlighting its cultural significance, key styles, and how its timeless creativity continues to influence modern artistry. Whether you’re an art enthusiast, a history lover, or someone wanting to learn more, discover how ancient art connects us to our roots and enriches contemporary creativity.
What Makes Ancient Art Special?
Unlike modern art, which often reflects personal expression or contemporary issues, ancient art was primarily a reflection of societal values, religious beliefs, and daily life. It served purposes beyond mere decoration—it was a storytelling medium, a record of history, and a tool for religious rituals.
- Cultural Documentation
Ancient art offers a glimpse into the traditions, customs, and values of civilizations long gone. A Greek amphora, for example, tells tales of heroic warriors, while an Egyptian fresco depicts ceremonies honoring the gods. These works preserve fragments of societies that have shaped human history.
- Craftsmanship with Tools of the Time
One of the most fascinating aspects of ancient art is the exceptional craftsmanship achieved with rudimentary tools. The precision of Mayan carvings or the intricate designs of Roman mosaics remains awe-inspiring, demonstrating the artists’ ingenuity and mastery.
- Timelessness
The masterpieces of ancient art have stood the test of time—both physically and culturally. The Great Pyramids of Giza, the Parthenon in Athens, or the cave paintings of Lascaux still evoke awe and influence new generations of artists, architects, and historians.
Understanding ancient art is not just about admiring its beauty; it’s about connecting with human innovation and the stories that continue to resonate today.
Styles and Mediums of Ancient Art
Throughout history, civilizations have developed distinct artistic styles and mediums based on their resources, beliefs, and societal needs. Here’s a closer look at some prominent forms of ancient art.
1. Cave Paintings
- Time Period: Prehistoric (as early as 30,000 BCE)
- Medium: Natural pigments such as charcoal, ochre, and hematite
- Notable Examples: Lascaux Caves (France), Altamira Caves (Spain)
These works, often depicting animals and human figures, are among the earliest examples of human creativity. Many are believed to have spiritual or ritualistic significance, aiming to connect hunters with their prey or invoke divine favor.
2. Ancient Egyptian Art
- Time Period: 3100 BCE – 30 BCE
- Medium: Limestone, papyrus, gold, and paint
- Notable Examples: Wall paintings in tombs, statues of pharaohs
Marked by strict conventions, Egyptian art prioritized symmetry and proportion to convey perfection and divine order. Each detail, from the size of the figures to their movements, carried symbolic meaning.
3. Mesopotamian Reliefs
- Time Period: 3000 BCE – 538 BCE
- Medium: Stone and clay carvings
- Notable Examples: Assyrian palace reliefs
Known for their intricate engravings, Mesopotamian reliefs often depicted scenes of gods, warriors, and royal conquests, emphasizing power and divine protection.
4. Ancient Greek and Roman Sculptures
- Time Period: 800 BCE – 476 CE
- Medium: Marble, bronze
- Notable Examples: The statues of Venus de Milo and Augustus of Prima Porta
Greek and Roman artists mastered human anatomy to create life-like sculptures that conveyed emotions and movement. While Greek art often celebrated idealized beauty, Roman works emphasized realism and individual character.
5. Mesoamerican Art
- Time Period: 1500 BCE – 1521 CE
- Medium: Jade, basalt, clay
- Notable Examples: Olmec heads, Mayan glyphs, Aztec sun stones
Mesoamerican art is highly symbolic, often tied to cosmology and religious rituals. Large-scale structures like pyramids and sculptures illustrate their advanced engineering and artistic skills.
The Cultural Significance of Ancient Art
Ancient artz wasn’t created in isolation. It reflects the cultural, economic, and religious fabric of its time. Here are three key cultural impacts:
- Religious Expression
From the grand Hindu temples of India to the serene Buddha statues across Asia, ancient artworks often served religious purposes. They were visual representations of devotion, serving as conduits to the divine.
- Social Hierarchy
Art often communicated power and authority. For instance, the grandeur of the Egyptian pyramids symbolized the pharaohs’ godlike status, while the life-sized statues of Roman emperors portrayed supreme control.
- Storytelling
Before written language became widespread, art conveyed stories and lessons. The Aboriginal rock paintings in Australia, for example, document ancestral tales passed down through generations.
How Ancient Art Influences Modern Creativity
The influence of ancient artz extends far beyond history books and museum walls. Its timeless creativity serves as a foundation for modern artistic and architectural endeavors:
- Artistic Techniques
The fresco techniques perfected by Renaissance artists have roots in ancient Roman and Greek methods. Similarly, the use of proportion and balance in visual arts owes much to classical traditions.
- Symbolic Design
Themes such as heroism, divinity, and nature borrowed from ancient motifs inspire contemporary artists and designers. Many fashion collections and visual media incorporate ancient symbols and aesthetics.
- Architecture
Modern architecture often draws inspiration from structures like Roman aqueducts, Greek columns, and Egyptian obelisks. These timeless designs continue to shape skyline silhouettes.
Preserving Ancient Art for Future Generations
To appreciate ancient artz is to recognize its fragility. Many of these works are susceptible to natural decay, environmental changes, and human interference. UNESCO and other conservation groups actively work to preserve this cultural legacy, but we all share a responsibility to support such efforts.
Whether visiting a historical site or supporting digital preservation projects, your efforts contribute to making these treasures accessible to future generations. Consider exploring virtual tours or donating to organizations dedicated to safeguarding world heritage.
Your Connection to Timeless Creativity
Ancient artz is a bridge between humanity’s past and present. It reminds us where we’ve been and inspires us to imagine where we could go. By understanding and appreciating its stories, techniques, and enduring beauty, you become part of an artistic lineage that stretches across millennia.
Explore these wonders not just as artifacts but as vibrant ties to human history. Visit museums, attend exhibitions, or engage in conversations that deepen your connection to the timeless creativity of ancient art.
Unlock the inspiration waiting for you in history’s masterpieces.
Final Thoughts
Ancient artz is more than a window into history; it is a testament to human ingenuity, perseverance, and the shared desire to create meaning through beauty. By exploring these masterpieces, we connect with the aspirations, struggles, and triumphs of those who came before us. Whether through careful preservation, active engagement, or a deeper understanding of its significance, we have the power to ensure that this legacy thrives. Let ancient art remind us not only of our past but also of our potential to shape a future where creativity and culture remain deeply valued.
Conclusions
The study and appreciation of ancient art reveal remarkable insights into humanity’s shared heritage and enduring creativity. By cherishing these works, we honor the cultures that formed the foundation of modern civilization while preserving their legacy for future generations. Ancient art teaches us that the pursuit of beauty and meaning transcends time, reminding us of the timeless power of creativity to unite and inspire. It is our responsibility to continue safeguarding this cultural wealth, ensuring that its lessons and wonders remain accessible to all who seek them.
FAQs
What is ancient art?
Ancient artz refers to the creations of early civilizations, including sculptures, paintings, pottery, architecture, and other artistic expressions. These works provide insight into the beliefs, traditions, and daily lives of past societies, often functioning as both artistic endeavors and practical tools or ceremonial objects.
Why is ancient art important?
Ancient artz holds immense cultural, historical, and educational value. It connects us to the origins of human creativity, offering a window into the evolution of culture and society. By preserving and studying these works, we gain a deeper understanding of our collective past and the foundations of modern civilization.
How can we preserve ancient art?
Preserving ancient artz requires a combination of scientific techniques, responsible stewardship, and public awareness. This includes the use of advanced conservation methods, protection against environmental damage, and the enforcement of laws to prevent theft or illegal trade. Additionally, promoting awareness and funding for preservation efforts helps ensure the survival of these treasures.
Where can ancient art be viewed?
Ancient Artz can be viewed in museums, archeological sites, and online digital archives. Many renowned institutions, such as The Louvre, The British Museum, and The Metropolitan Museum of Art, house extensive collections of ancient art from across the globe, providing access to these masterpieces for scholars and the public alike.
Blog
Modern Real Estate Trends Shaping Residential Living
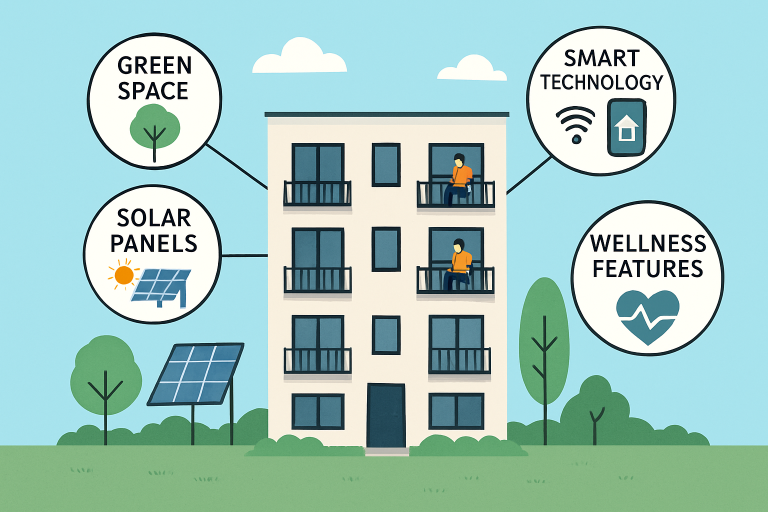
Today’s residential real estate market is undergoing a dynamic transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving work habits, and shifting lifestyle preferences. Buyers and renters increasingly seek homes that accommodate remote work, technological convenience, and environmentally friendly designs. These modern shifts are evident in thriving markets such as Aspen, where high-end living intersects with the latest housing trends. For those interested in premier properties designed with today’s standards in mind, explore Aspen Homes for Sale for a glimpse of homes that embody these progressive features.
Whether looking for a high-rise apartment with wellness amenities or a smart home with energy-saving technology, consumers now demand flexibility and innovation. Factors such as sustainability, community-oriented living, and digital engagement play pivotal roles in how developers design and market new residences, shaping the future of where and how people live in both urban and suburban areas. With market pressures and environmental concerns, homebuilders prioritize innovations that increase efficiency and foster community. This holistic approach enhances property values and residents’ well-being. In leading cities and luxury destinations alike, these trends are steering the market toward greener, smarter, and more connected homes.
Staying ahead of these shifts is crucial for both buyers and industry professionals. According to a recent analysis by The New York Times Real Estate Section, incorporating flexibility and sustainable solutions adds long-term value to residential investments.
Smart Home Integration
The adoption of smart home technology has moved from novelty to necessity in many residential markets. Integrated systems for lighting, climate control, and security deliver unparalleled convenience and can significantly reduce energy consumption. Many buyers expect to see smart thermostats, remote-controlled appliances, and app-based monitoring as standard features. Not only do these technologies streamline everyday living, but they also enhance security and create personalized comfort tailored to each occupant.
Remote Work and Home Office Spaces
The remote work revolution has made dedicated office spaces a central consideration for homebuyers and renters. Flexible floor plans, soundproof rooms, and custom workstations are sought-after features in both new builds and renovation projects. Developers are also introducing multipurpose rooms and modular furnishings, allowing for adaptation as working styles continue to shift. This reflects a broader trend of homes built to serve diverse professional and personal needs without compromising on comfort or style.
Sustainable Building Practices
Growing awareness of climate change and rising utility costs has made sustainable building practices a top priority. Developers now incorporate recycled materials, solar panels, advanced insulation, and other green building technologies. These efforts minimize environmental impact while providing residents with lower energy bills and healthier indoor environments. Additionally, sustainability certifications add tangible value to properties and attract eco-conscious buyers.
Co-Living Arrangements
As urban populations rise and real estate prices soar, co-living has emerged as a practical and social alternative, particularly for young professionals and digital nomads. These communities offer private living spaces coupled with shared kitchens, lounges, and recreational areas. Such arrangements not only provide cost savings and flexibility but also create networks of support for newcomers to a city or those seeking communal experiences.
Social Media’s Impact on Real Estate Marketing
Technology has revolutionized not just the homes themselves but also the way they are bought and sold. Real estate professionals harness platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook to create immersive virtual tours and reach wider audiences. Social media-driven marketing methods can increase visibility, generate buzz around listings, and enhance engagement with buyers, sellers, and industry partners. According to The Wall Street Journal Real Estate, these platforms now influence every stage of the transaction process, from discovery to negotiation.
Emphasis on Wellness Features
Health and wellness features now play a central role in modern residential design, as home buyers increasingly prioritize spaces that support balance and well-being. Dedicated home gyms, quiet meditation rooms, and spa-inspired bathrooms encourage daily exercise, stress reduction, and self-care. Designers are also emphasizing natural light, indoor plants, and seamless access to outdoor terraces to improve mood and air quality. Together, these elements create homes that nurture physical vitality and mental clarity for modern lifestyles.
Urban Verticalization
Vertical living solutions address limited space and the growing demand in busy metropolitan areas. High-rise residential towers maximize land use while offering premium amenities, panoramic city views, and close access to broader hubs and cultural destinations. Many developments incorporate shared features such as rooftop gardens, lounges, and fitness centers. These elements recreate aspects of suburban comfort within a smaller footprint, encouraging social interaction, convenience, and a strong sense of community in dense urban environments worldwide.
Conclusion
Modern real estate trends are driven by innovation, adaptability, and a deep understanding of changing consumer needs. From smart home integration and sustainable building practices to wellness-focused layouts and digitally powered marketing, these developments are redefining residential living. By staying informed and embracing these trends, buyers and industry stakeholders can navigate a rapidly evolving landscape and secure lasting value in their investments.
Blog
How Pipe and Valve Systems Keep Modern Industries Flowing Safely
In the intricate web of modern industry, pipe and valve systems are the unsung heroes, quietly ensuring the seamless, efficient, and safe transport of fluids and gases that power our world. Whether it’s oil in a refinery, steam for manufacturing, or clean water for municipal use, these systems are fundamental to keeping countless processes moving smoothly behind the scenes. The reliability of these essential components directly influences the productivity, sustainability, and safety of critical infrastructure. Companies such as Mattsco Supply Company, a leading industrial piping company Tulsa, OK, have played a pivotal role in this field, supplying high-quality piping solutions since 1975. Their commitment to innovation and service underlies much of the safety and efficiency seen in industries today.
The Backbone of Industrial Operations
Pipes and valves function much like the circulatory system in the human body: they direct, control, and regulate the flow of essential substances throughout industrial complexes. These systems, which carry chemicals, oil, gas, or water, are found at the core of power plants, refineries, food processing facilities, and healthcare institutions. Their careful design and the choice of materials are absolutely vital to withstand the sometimes extreme pressures, temperatures, and chemical characteristics of the transported media. For instance, specialized alloys and polymers might be chosen to resist corrosive chemicals or intense heat.
Advancements in Materials and Technology
Materials science has greatly enhanced the scope of piping and valve applications. Traditional materials, such as steel, iron, brass, and copper, have been supplemented or even replaced with advanced plastics and composite materials. Among the most prominent innovations is Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride (UPVC), valued for its combination of strength, chemical resistance, and lightweight structure. UPVC valves and piping components have revolutionized fluid control, enabling faster installations, reducing maintenance costs, and ensuring longer operational life, especially in corrosive chemical environments. Their resistance to scaling and fouling also makes them ideal for potable water and food industries, where cleanliness and purity are paramount. Furthermore, the flexibility and modularity of modern fittings enable easier system expansion and modification, supporting the dynamic needs of industrial operations.
Integration of Smart Technologies
The digital transformation sweeping across industries has fully reached the world of pipe and valve systems, ushering in a new era of automation and intelligence. The incorporation of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into these systems has fundamentally changed how industries approach system reliability and risk management. Smart sensors, embedded throughout the piping network, continually monitor parameters such as pressure, temperature, and flow rates. Data from these sensors can be analyzed in real time, providing operational teams with instant alerts when readings move outside safe thresholds. As a result, issues such as leaks, blockages, or abnormal wear can be identified and addressed before they escalate into more costly problems. Predictive maintenance, powered by advanced analytics and machine learning, enables companies to schedule servicing only when it is truly needed, reducing routine shutdowns and significantly lowering the risk of unplanned downtime. Ultimately, this integration of smart technology enhances operational efficiency and workplace safety, resulting in significant time and resource savings throughout a system’s lifecycle.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
No matter how advanced the technology or material, all pipelines and valves require routine inspection and thoughtful maintenance. Over time, natural wear and tear, exposure to harsh substances, and mechanical stress can compromise the integrity of these systems. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and periodic replacement of worn components, helps identify emerging issues before they lead to leaks or catastrophic failures. Valves, in particular, are critical because they directly control fluid flow and pressure and must remain responsive and tight-sealing. Neglecting maintenance not only risks significant operational disruptions but can also pose serious safety hazards, threatening both workers and the environment. For this reason, many industries invest in comprehensive maintenance programs that use both traditional physical inspections and remote monitoring data to keep their systems in peak condition year-round, thus extending equipment lifespan and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Industrial piping and valve systems are subject to a host of regulations and standards, designed to protect workers, communities, and natural resources from potential hazards. Adhering to these standards, whether set by industry organizations, government bodies, or international agencies, is a non-negotiable aspect of system design, installation, and operation. For businesses, compliance ensures that their systems are robust enough to handle industry-specific demands, from volatile chemicals in chemical plants to sanitary requirements in food processing. The consequences of non-compliance can be severe, including legal penalties, environmental damage, or the loss of business licenses. Moreover, prioritizing safety and regulatory compliance also builds trust with customers and the public, cementing a company’s reputation as a responsible industry leader.
Conclusion
Pipe and valve systems remain the fundamental infrastructure that enables the safe, efficient operation of the world’s most vital industries. Through continued advancements in materials science and smart technologies, these systems have become safer, more reliable, and easier to maintain than ever before. Companies that commit to regular maintenance, rigorous safety protocols, and compliance with ever-evolving industry standards will ensure that their piping networks not only keep pace with technological change but also continue to safeguard workers, communities, and the environment. The future of industry depends on the invisible work of pipes and valves, and the ongoing innovation and care invested in their design and upkeep.
Blog
How Digital Payment Solutions Are Changing the Way Businesses Manage Spending
The Shift Towards Digital Payments
In recent years, businesses of all sizes have accelerated the move away from traditional payment methods. The urgency for quicker, more secure, and more efficient ways to handle transactions has driven this change. Companies are replacing paper-based systems and manual processes with agile digital tools to keep up with evolving market demands. Startups and established enterprises alike are exploring more innovative options for expense management, including startup credit cards, which enable rapid, trackable spending.
Digital payment adoption is no longer seen just as a way to modernize bookkeeping but as a strategic lever to unlock business growth. According to a J.P. Morgan report, well over half of its global clients named the ability to support new business models through digital treasury operations as a leading priority. Swift, digitized payments create new opportunities for companies to improve their spending oversight and support organizational scalability (source).
As digital payment platforms become mainstream, their role in eliminating cash handling and paper checks is impossible to ignore. In addition to speeding up transactions, businesses adopting digital payment solutions gain deeper visibility into every outgoing dollar. Account teams can quickly reconcile payments, manage vendor relationships, and meet compliance obligations with far less manual intervention. These capabilities are essential for industries that have historically faced slow-moving payment cycles and cumbersome expense reporting.
Beyond convenience, digital payments reflect the expectation that business systems deliver transparency and flexibility. This shift is not limited to one sector. Companies across retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and technology stand to benefit from fully embracing digital payment workflows.
Enhanced Security Measures
Security is a primary reason businesses are prioritizing digital payment solutions. Unlike traditional checks or physical cash, digital payment platforms are typically equipped with multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and fraud detection tools. Real-time validation of account details helps ensure that funds reach intended recipients, reducing the risk of criminal activity. Many platforms also include customizable user permissions, so only authorized personnel can initiate or approve transactions.
With cyber threats continually evolving, best-in-class digital payment providers invest heavily in next-generation security protocols. Businesses adopting such solutions gain peace of mind while also simplifying compliance with regulatory standards. For example, automated audit trails and secure records make it easier to demonstrate appropriate financial controls during an external review or audit. According to PYMNTS, digital transformation is rapidly reshaping how financial services mitigate risk and prevent fraud.

Integration with Financial Management Tools
Beyond simple payment processing, leading digital solutions integrate directly with accounting, budgeting, and enterprise resource planning software. This convergence gives finance teams real-time access to data across accounts payable, expense management, and payroll functions. When companies connect digital payments to their broader financial management ecosystem, they gain the power to streamline reconciliation, automate reporting, and boost budgeting accuracy.
Automated alerts and dashboards enable businesses to monitor spending patterns in real time, surface unusual activity, and track budget adherence down to the department or project level. Many platforms also allow for customizable spending rules, enabling greater control over where and how funds are allocated. This proper integration offers organizations a significant advantage in forecasting expenses, understanding cash burn, and planning for future investment.
Cost Savings and Improved Cash Flow
One of the most significant advantages of digital payment solutions is their impact on operational efficiency and the bottom line. Companies can reduce costs associated with printing, mailing, and reconciling paper checks, all of which are labor-intensive and can be prone to error. Faster electronic payments also allow businesses to capture early-payment discounts offered by vendors or to improve their ability to negotiate favorable payment terms.
Quick, reliable cash flow is an essential ingredient for business health. Digital payments shorten the transaction cycle, so companies can access incoming funds sooner and allocate resources more strategically. These improvements often translate into fewer delays in supplier payments, better vendor relationships, and less administrative stress on finance personnel. As reported by Comerica, businesses that embrace a range of modern payment options are more likely to maintain resilient and predictable cash flow.
Adapting to Consumer Preferences
The rise of digital payment methods is not only a back-office revolution. It mirrors changing consumer expectations, who now demand fast, flexible, and secure options for completing transactions. Businesses that offer digital payments can deliver a superior customer experience, thereby driving loyalty and repeat business. Providing a range of payment options, including mobile wallets, contactless cards, and online invoicing, broadens the potential customer base and meets users where they prefer to transact.
The ability to process digital payments quickly and securely at checkout is particularly valuable for e-commerce and retail. Swift transaction experiences reduce friction, minimize abandoned carts, and build customer confidence in a brand’s ability to safeguard their financial information.
Challenges in Transitioning to Digital Payments
The journey to fully digital payments has its hurdles. Upfront investments in technology, configuring new systems, and staff training all present initial barriers for businesses making the transition. In some industries, legacy workflows and outdated infrastructure can slow down migration efforts. However, with forward-looking planning and support from experienced vendors, organizations can minimize disruptions and realize long-term benefits that significantly outweigh these short-term challenges.
Another consideration is the readiness of partners and suppliers. Not all vendors are equipped to accept digital payments immediately, so businesses must coordinate closely to avoid bottlenecks during implementation.
Future Trends in Digital Payments
As technology evolves, so do the features and functionalities of digital payment solutions. Digital wallets continue to grow in popularity, enabling both consumers and businesses to store payment information and initiate transactions instantly and securely. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also being leveraged to deliver more advanced fraud detection, automate reconciliation, and predict spending trends.
As regulatory environments change and fintech innovation accelerates, staying up to date on new developments is critical. Businesses that keep a finger on the pulse of digital payment trends are better positioned to adapt quickly, capitalize on advances, and remain competitive in their industries.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced financial environment, digital payment solutions offer far more than convenience. They enable companies to manage spending with greater precision, reduce risks, and prepare for long-term growth. The capabilities gained from embracing these technologies mean that businesses not only improve their day-to-day operations but also strengthen their foundation for the future. Those who adapt and innovate with digital payments are best poised to lead in the years ahead.
-

 Technology11 months ago
Technology11 months agoRevealed: 8093642079 – Find Out Who’s Behind the Number
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoHow Horseback Adventures Foster Connection and Wellness
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoDetecting AI-Generated Text: Tips and Techniques
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoRaterpoint: Revolutionizing Online Content Evaluation and Feedback
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoFDXMZ24: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 Entertainment1 year ago
Entertainment1 year agoFappelo: How to Engage with This Exciting New Phenomenon
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoPerchance AI | Intelligent AI Solutions for Your Business
-

 Blog1 year ago
Blog1 year agoBunkralbum: What You Need to Know About This Intriguing Concept
